Disruptor Illustrated by Metaphor
What is disruptor
LMAX disruptor is a high performance alternative to bounded queues for exchanging data between concurrent threads. Disruptor is first applied in financial and messaging systems for its high performance.
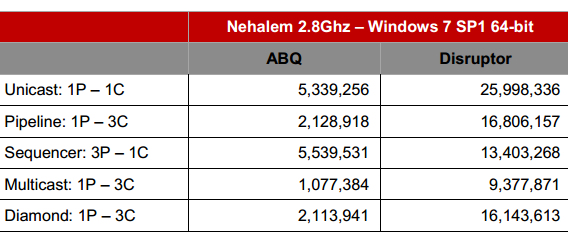
Disruptor throughput compared to queue
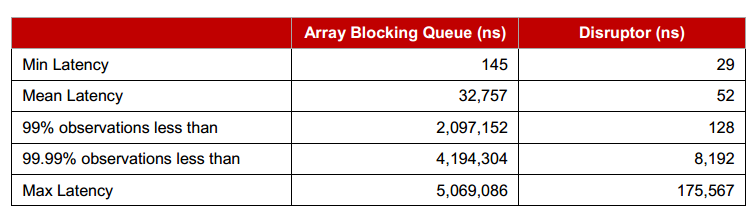
Latency compared to queue
Showing mechanical sympathy to modern CPU designs, disruptor is so fast in a parallel and staged environment. Following explains this in detail.
Parallel Programming
The best way to explain technology is by metaphor. As is said:
Technology is similar, thought behind is the key.
Metaphor in real world
You are the boss of a fast food restaurant, what are you supposed to do to serve more customers? You hire a waitress with fast hands.
Waitress with fast hands

However the speed of waitress is limited, so you hire another waitress. Now the two process requests in parallel, and total throughput is doubled.
Hire two waitresses
Technology
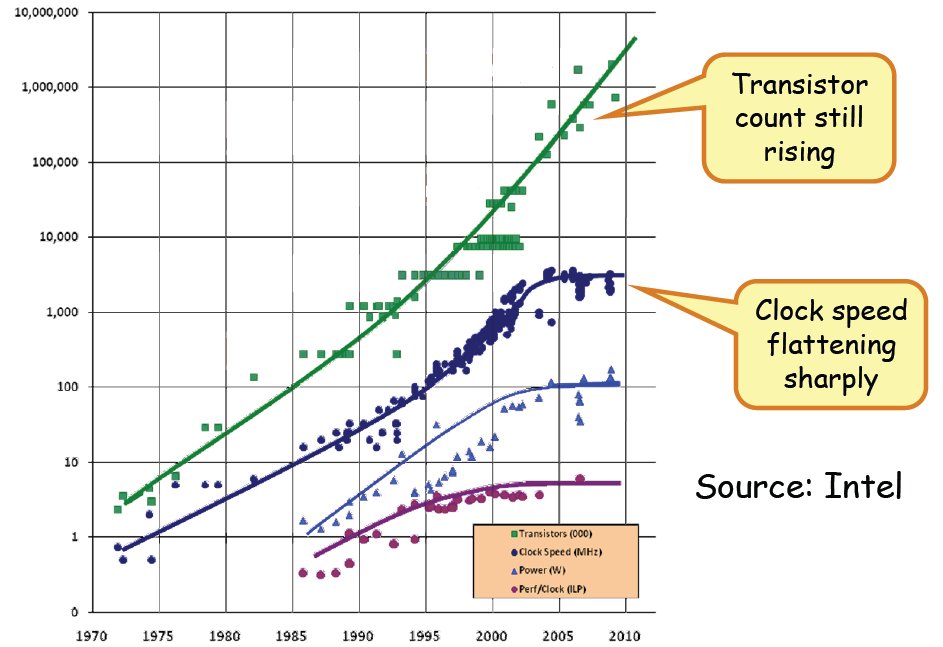
Parallel programming is just the same. with a high speed CPU, programs can run fast, result in high throughput and low latency. However CPU speed is limited to several GHZ, so more CPU cores are introduced, and programs can run in parallel.
CPU speed is limited, but the core numbers obey Moore’s law
Staged processing
Metaphor
Your restaurant grows rapidly, so you must extend your business to more cities, even more countries. As the boss you can not manage all of your employee by yourself, instead you hire managers.
an organization is composed of multiple stages
Technology
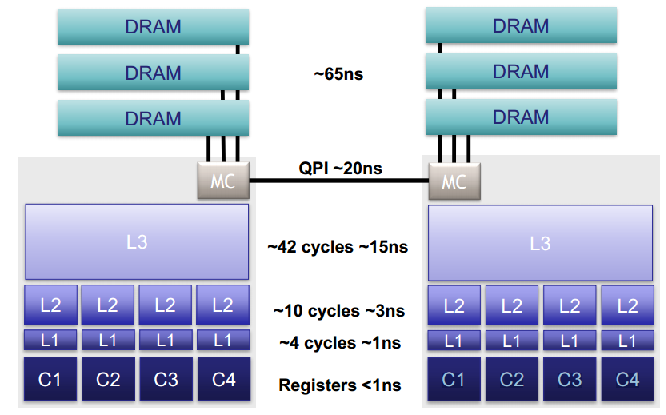
Modern CPU has multiple level caches, and the architecture is similar to an organization.
CPU cache contains multiple stages
Amdahl’s law
Metaphor
In real world there is all kind of inefficiency, one department may depend on another. That’s why management theories exists.
Technology
In a program, how can we optimize process in such a parallel and staged environment?
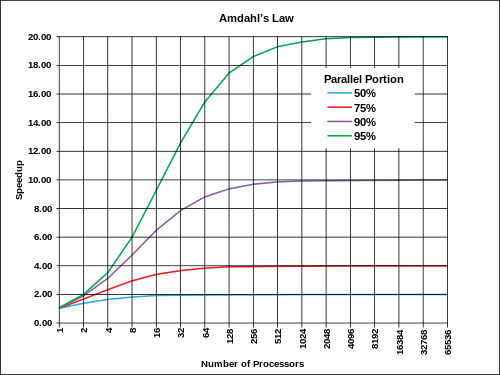
Amdahl’s law
The speedup of a program using multiple processors in parallel computing is limited by the time needed for the sequential fraction of the program. If %5 of the program cannot compute in parallel, the speedup can only reach 20 times no matter how many processors there are.
Amdahl’s law
To remove inefficiency, just find the bottleneck that can not run in parallel, namely avoid shared resources.
Optimization: Batch message
The first bottleneck is main memory access, which is expensive.
Metaphor
Manager collect status of employees, but they do not send to the boss you one by one, instead they wait until all the status are collected, and send to you in a batch.
Technology
Similarly, CPU cache is split to cache lines, and batch read data from main memory.
Disruptor use ring buffer to place objects padding together in memory so as to avoid false sharing and cache miss.
Ring buffer
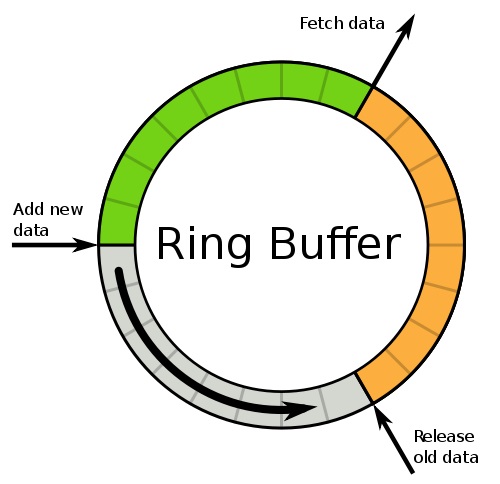
Optimization: Lock free synchronization
Another bottleneck is shared locks.
Metaphor
People manager and product manager both manage employees. They can exchange status of employees directly since their offices are close to each other.
Technology
Synchronization for shared resource is expensive.
- Lock: involves context switch, which is quite expensive.
- CAS: lock instruction pipeline and complex to program.
lock penalty
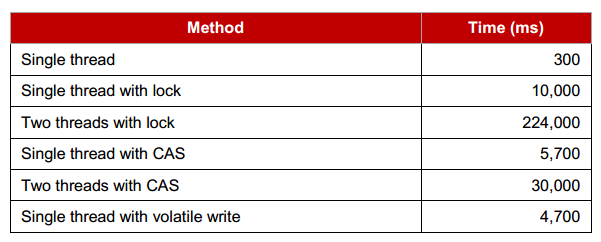
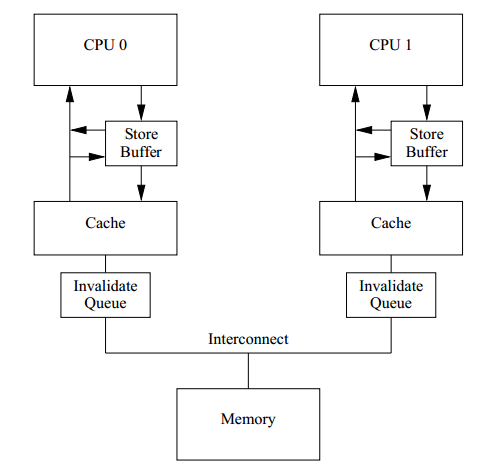
Disruptor use lock free memory barrier to synchronize sequence of ring buffer. Two cores in CPU talk to each other directly via memory barrier to exchange resource state, so as to avoid accessing shared locks.
memory barrier